Winning team: McKinley Mills for the New Millennium
Team members: Emily Talen, Defne Aksel, Justin Bologna, Fabienne Bick, Andrew Goldblatt, Griffin Seyfried, Isaac Rand, Andrew Langford, Julia Spande - University of Chicago
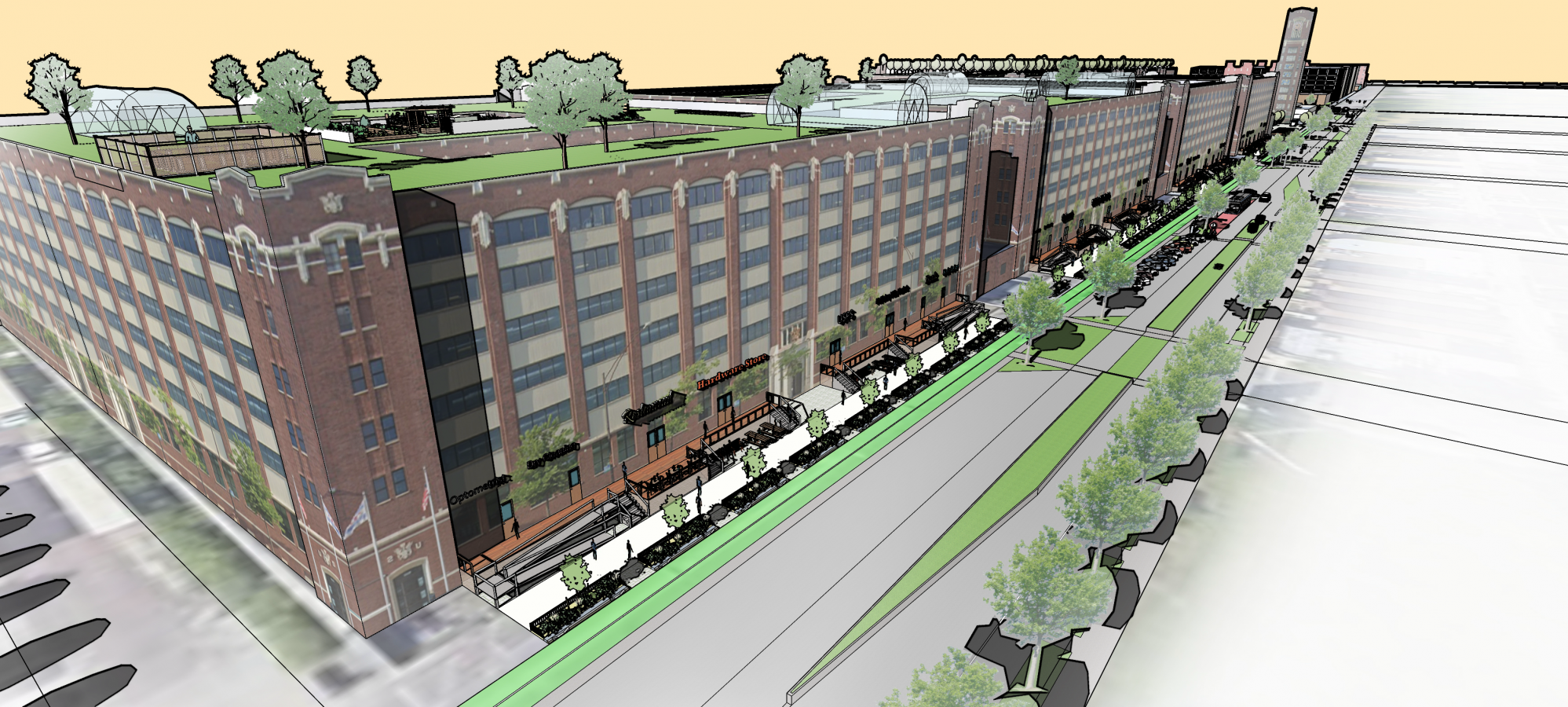
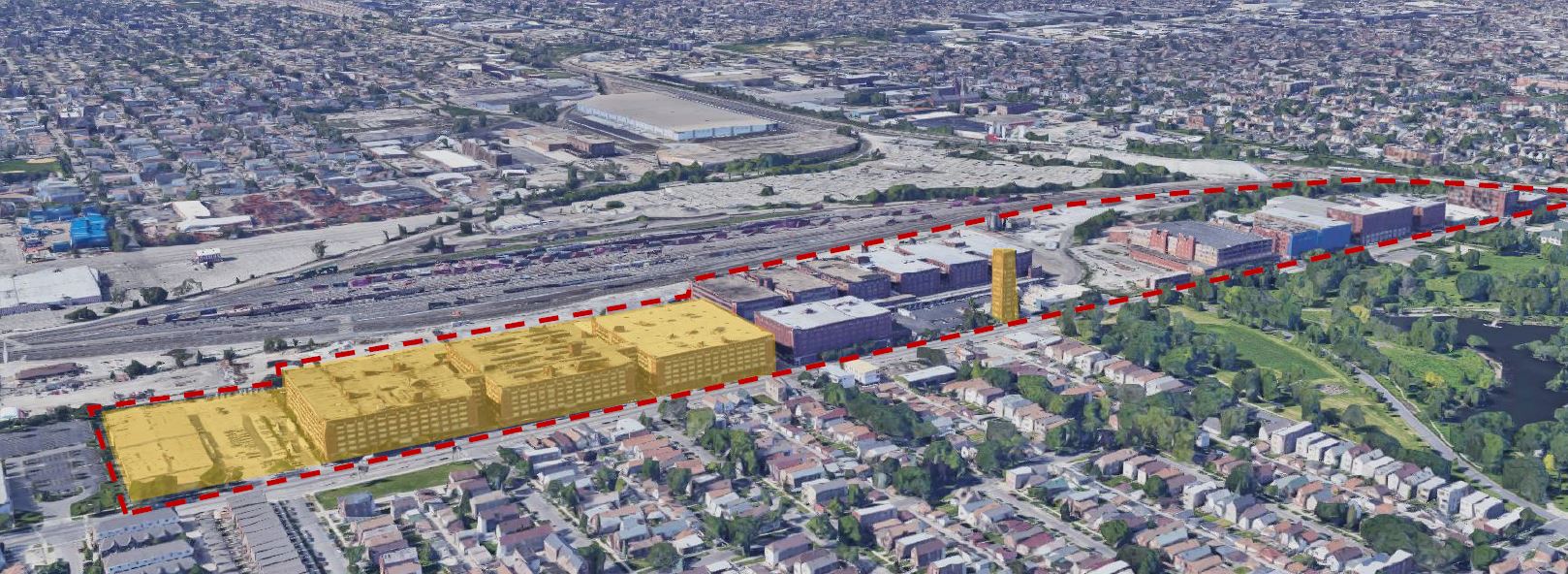
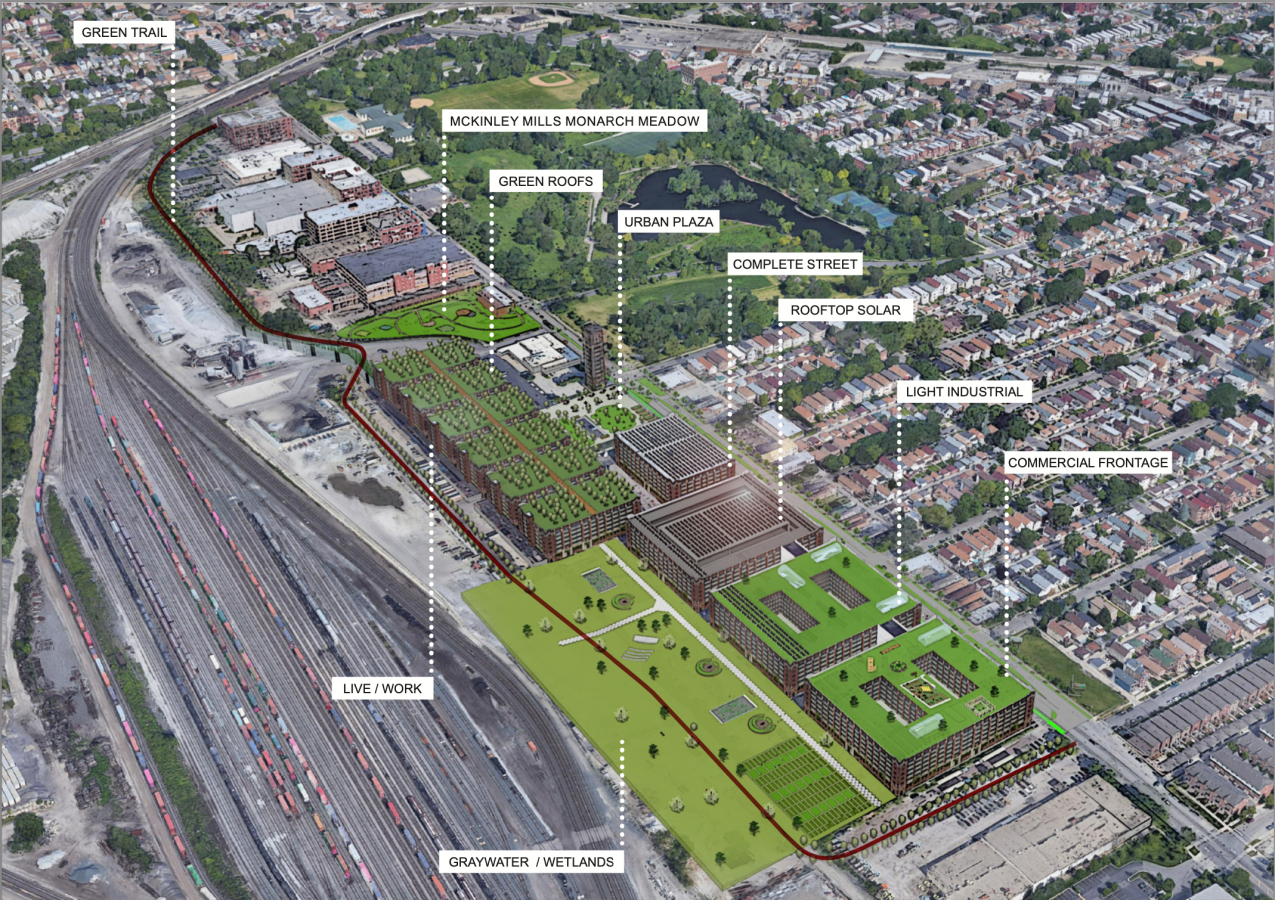
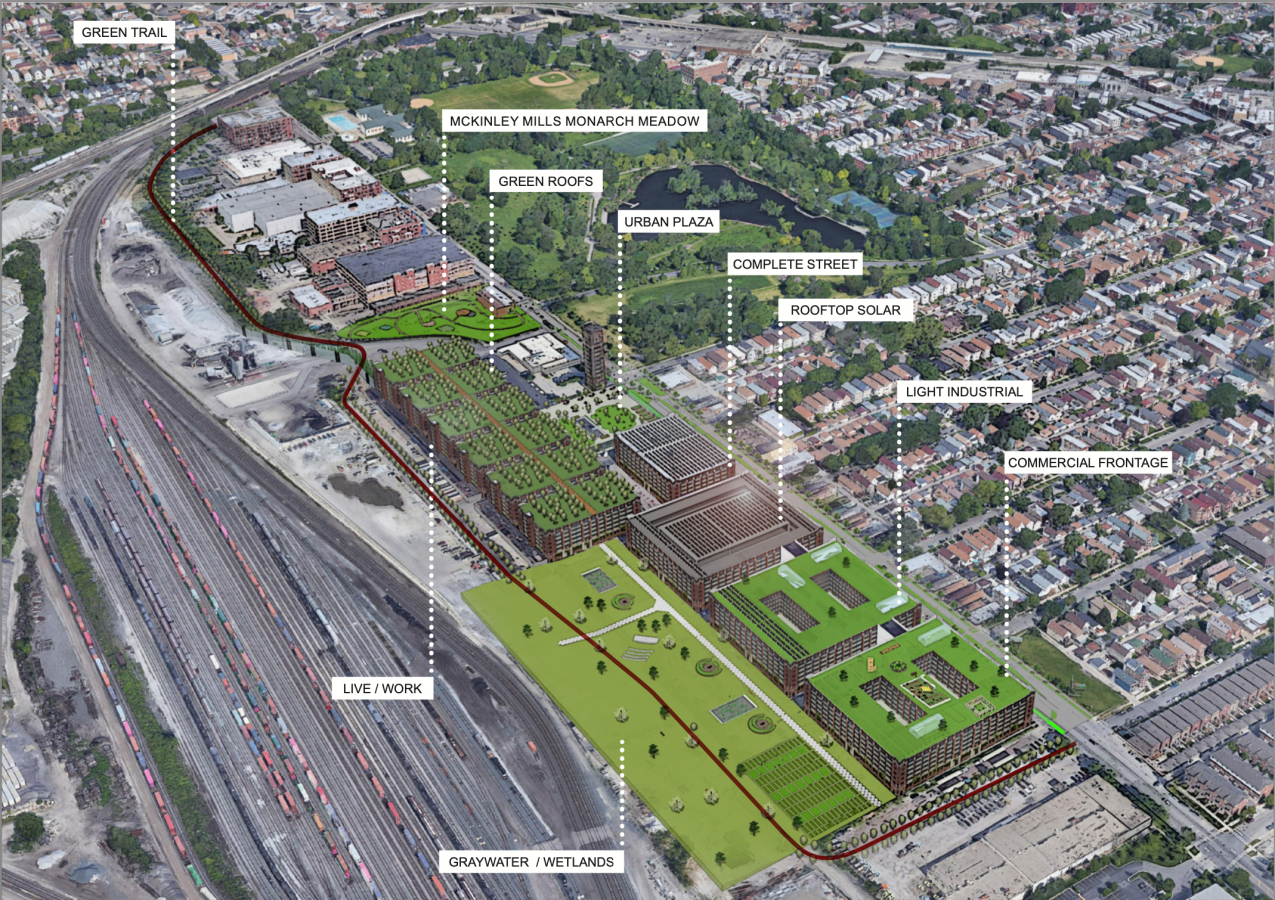
The team reinvented and revitalized a disused, formerly industrial site in Chicago’s McKinley Park neighbourhood as a mixed-use, sustainable community. The project anchored its interventions through revitalization of existing buildings and developing new residential and commercial units. These units incorporate adaptive reuse and clean, efficient construction methods with the aim to minimize emissions. The proposed green infrastructure includes permeable pavement, green roofs, wildflower meadows, and constructed wetlands. In addition, solar companies will provide training and middle-class, green-collar jobs to the community.
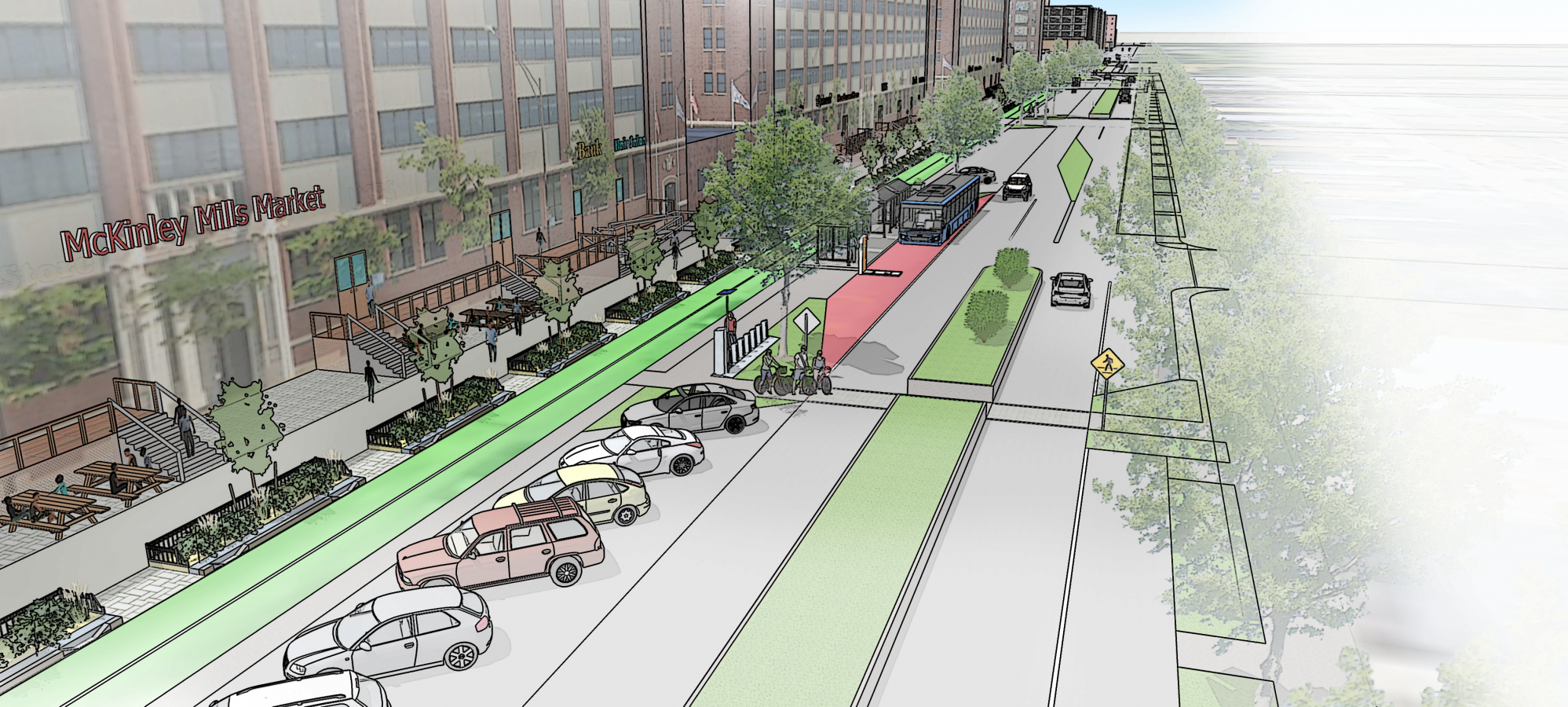
Connectivity is maximized between the site and the McKinley Park community through the major streetscape and facade alterations, which make the area much more pedestrian-oriented. An analysis of existing resources in the area guided the team’s decision to include a grocery store, a daycare, and a community health clinic.
Key components
-
The redevelopment plan seeks to activate ground floors with commercial activities. This development comprises 48 commercial spaces and a sidewalk redesign.
-
The site will integrate solar energy in three distinct ways: solar green roofs, a social access solar garden, and freestanding solar arrays in converted parking lots.
-
To manage water two 15,000-gallon concrete rain cisterns will be located underground next to the constructed wetlands. The reuse of non-portable water through on-site wastewater treatment.
-
Implementation of on-site recycling practices in high-rise residential and commercial buildings.
Learn more about the project in the project presentation .
Presentation of the site
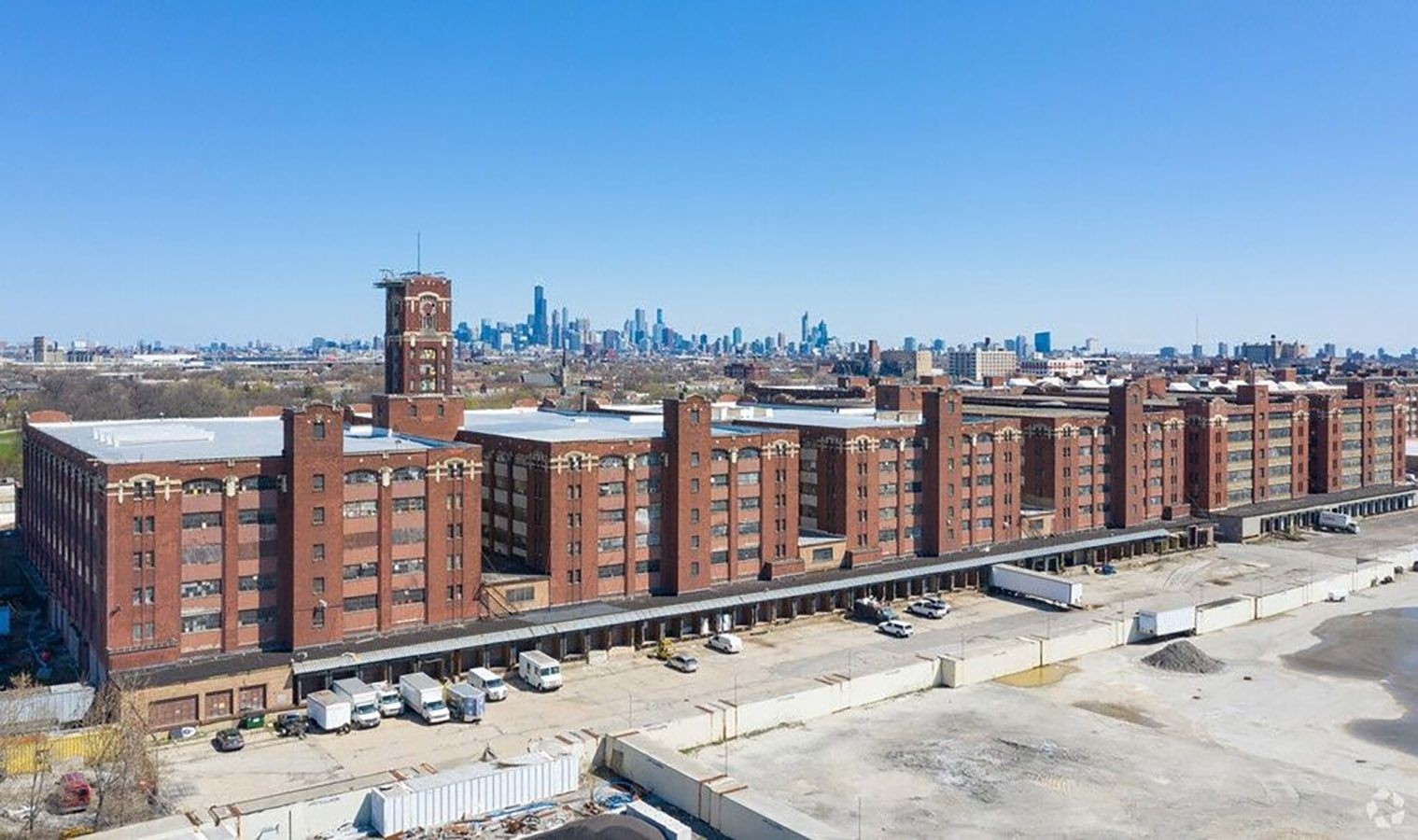
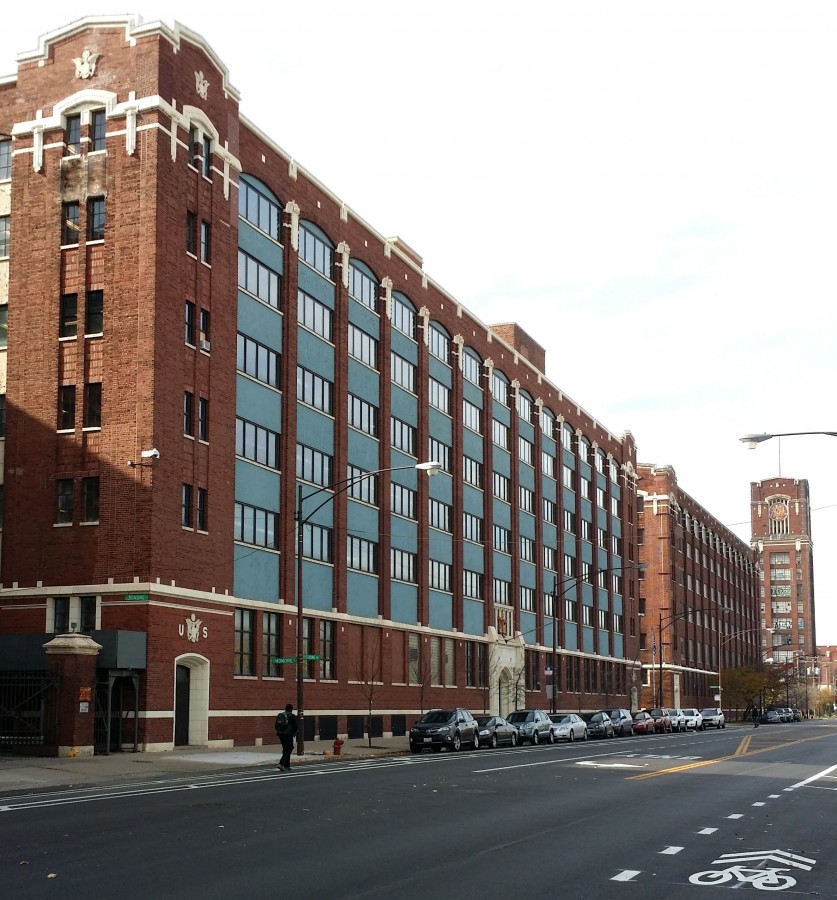
The Pershing Road Central Manufacturing District (“District”) is located in Chicago, Illinois, in McKinley Park, a stable, working class neighborhood on the city’s south-west side. The District is located in an area of transitioning land uses, with active industrial to the south, and residential neighborhoods and a destination park to the north. In recent years, several buildings in the District have been redeveloped into non-industrial uses.The District includes nearly one dozen industrial buildings, built around 1918. Over recent years, several buildings within the District have redeveloped into non-industrial uses, but redevelopment has been piecemeal and disconnected from the broader context.
The City of Chicago seeks a master plan and cohesive vision for the District, which unifies current and potential future land uses, identifies adaptive reuse opportunities, incorporates Green and Just recovery principles, and positions the District for future success, with a particular focus on opportunities for the re-development and adaptive reuse of city-owned property.
The vision should serve as an example for supporting Chicago’s Climate Action Plan to reduce dependence on fossil fuels, greenhouse gas emissions, and reinforce key Green Urban Design strategies to capture rainfall. Since 2018, the City has partnered with C40 on a previous Reinventing Cities competition for the city-owned property that was not successful, and has also worked to identify mitigation strategies for an existing asphalt plant that impacts the area.
Approx. site area
60 acres/24.5ha
Demographics
Population of 15900. 17% white, 56% Hispanic or Latino and 25% Asian. 15% of area residents work in the service industry, 11% in retail, and around 9% work in manufacturing 70% of residents leave the neighborhood for employment